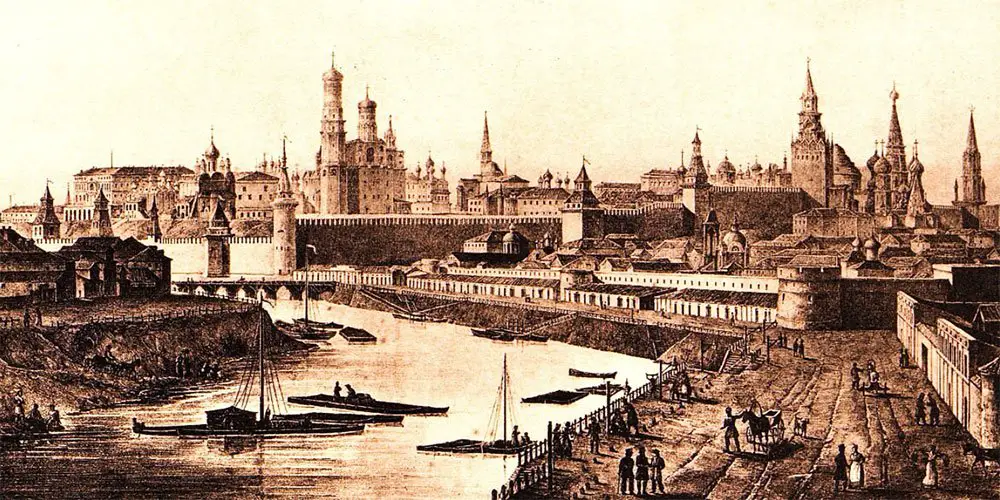
The Moscow Kremlin has long been the main symbol of Moscow and Russia – and for good reason. It was with the Kremlin that city of Moscow officially began and from which it grew. The Prince of Moscow, ruling from the Kremlin and drawing on the growing power of his city, united and conquered the cities and lands around him to create Russia.
While the Kremlin can be seen as something of a constant in Russian history, the Kremlin itself has seen major changes within its walls and to its own status. It has lost and gained buildings. It has changed from the seat of government to an ancillary structure, back to the governmental seat, and finally to a museum complex.
The resource below unites the work of multiple SRAS students writing on Home and Abroad, Challenge Grants, and Online Research Internships to bring you an overarching view of this iconic complex.
The Kremlin Walls
By Hudson Dobbs
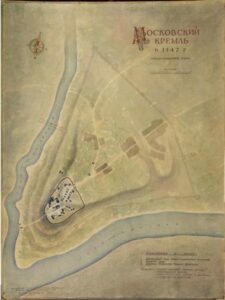
The Kremlin was first established in 1156 by Prince Yuri Dolgorukiy. This post-dates the first mention of Moscow, which dates back to 1147, when Prince Dolgorukiy invited Prince Sviatoslav of Chernigov to Moscow to celebrate their alliance.
The actual site of this stronghold has likely been occupied since the second millennium BCE. It likely had fortifications built there as early as the 10th century, by the then-resident Vyatichi, a tribe of Slavic peoples.
Eventually, Prince Dolgorukiy ordered the construction of what would become the Kremlin walls. These first walls were tall and expansive and built out of wood. Although this structure was built for protection, it also served as a symbol for the power and strength of the new city of Moscow.
While the first walls did their job well, they were eventually burnt down by Tatar-Mongol forces and later upgraded to more fire-resistant oak in 1339. As the city grew, the Kremlin also further developed, and with it the popularity of building fortresses in town centers. Cities such as Smolensk, Kazan, Novgorod, and Pskov all constructed a Kremlin of their own. In fact, the word “kremlin” simply means “a fortress within a city.”
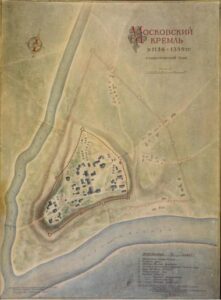
By the 13th century, the Kremlin housed the political and spiritual power of the state, with residences, workshops, churches, and state buildings all residing within its walls. In the 1360’s, Prince Dmitry Donskoy rebuilt the walls in limestone and a gleaming white Kremlin soon became the iconic image of Moscow. These walls were credited in helping the city defend itself from sieges by Grand Duke Algirdas of Lithuania in the late 1360’s.
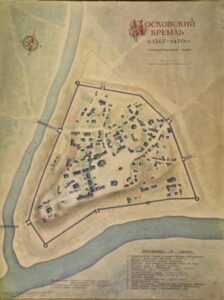
The walls and towers that exist today are still another iteration, and were built on the order of Grand Prince Ivan III, also known as Ivan the Great, from 1485 to 1495. Ivan wanted to build something grander and more worthy of being his residence – something that would be comparable to Constantinople in terms of size and importance.
Wanting what would be specifically a “Third Rome,” Ivan invited Italian architects such as Aristotele Fioravanti and Pietro Antonio Solari. Their involvement is why the current fortress closely resembles castles of Northern Italy. Its red brick made the Kremlin unique for the time, as it was the first structure in Russia built from such material.
These brick walls have stood, with minor adjustments, since that time. One noticeable change came in the late 1600s, when Tsar Fyodor Alekseevich ordered the red brick to be whitewashed in limestone, returning it to gleaming white the city had been hitherto known for. Eventually, the whitewash stopped being maintained and was allowed to wear off, a process that was complete by the 1900s.
The Kremlin Churches of Cathedral Square
By Serena Keenan
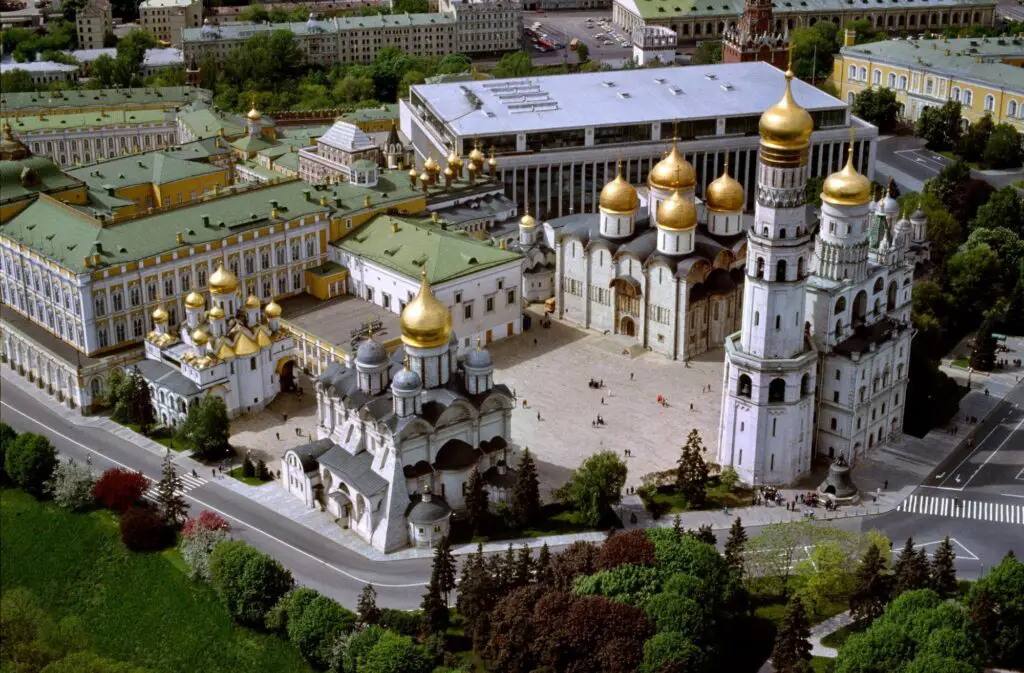
Cathedral Square is an area inside the Kremlin walls that is surrounded by many different churches that are all hundreds of years old. This is the area of the Kremlin that has remained relatively unchanged during its long history.
Each church on Cathedral Square was an active church until the Russian Revolution of 1917. Those that survived the Soviet period often did so as “museums of architecture” or as repurposed space. After the collapse of the Soviet Union in the early 1990s, some were given back to the Orthodox Church and resumed services, while others remain part of the Kremlin’s museum complex. Today, the churches are open to the public, although some are accessible by private tour only.
The Dormition Cathedral (Успенский Собор; also sometimes called the Assumption Cathedral), is the oldest of the Cathedral Square churches. It is named after the Dormition of the Virgin Mary, which is also the name of a Great Feast Day in Russian Orthodoxy. It commemorates when the Mother of God “fell asleep” and her body ascended directly to heaven.
Built in 1475, the Dormition Cathedral is the burial place of nineteen Orthodox patriarchs and metropolitans from the 14th to the 18th centuries. It also served as the coronation place for every Russian tsar, even after the founding of St. Petersburg. The site continues to be culturally and politically significant for Russian leaders, with President Putin visiting the cathedral for prayer services with the Russian patriarch after his inaugurations.
Architecturally, the Dormition Cathedral houses a five-tier iconostasis designed by Dionisy, as well as images of Christ the Pantocrator, Nikita and John of Novgorod, The Virgin of Vladimir, the angels Gabriel and Michael, and other iconography. After the fire of 1547, its five gilded cupolas were reconstructed with gold sheeting. Overall, the architectural style is a blend of Russian and Eastern European.
The Annunciation Cathedral (Благовещенский Собор) is named after another significant moment in the life of Mary, when she was told by an angel that she would conceive Christ. This church was designed in 1484 by architects from Pskov, then one of Russia’s great cities. The Annunciation Cathedral is one of the oldest examples of Russian art and architecture, since the majority of churches on Cathedral Square (including the Dormition Cathedral), were built with the involvement of Italian architects. This church functioned as a private facility for the royal family, and restarted religious services in 1993. It boasts nine gilded domes and one of the oldest surviving iconostasis in Russia, with six-tiers and nearly 100 icons.
The Archangel Cathedral (Архангельский Собор) is in the southeast corner of Cathedral Square. It’s named after the Archangel Michael, who is believed to be the protector of Russian leaders. It was often visited by those leaders to pray for good luck before war. The cathedral also functions as the burial place for nearly all of Russia’s tsars, starting with Ivan III (who was the first to use the term, although then still unofficially) and ending with Feodor III. After Feodor, Peter the Great moved the capital – and the final resting place of the tsars – to St. Petersburg. Consecrated in 1508, the Archangel Cathedral is a particularly opulent example of Byzantine-Russian architecture. Its iconostasis includes a depiction of the Archangel Michael painted in 1399.
The Ivan the Great Bell Tower Complex (Колокольня Ивана Великого) is perhaps the most recognizable element of Cathedral Square. It is the tallest structure within the Kremlin and thus is a prominent part of the Kremlin’s famous skyline. Built between 1505-08, it was inspired by Italian campaniles and was the tallest building in Russia at one point. Though not a place of worship itself, the tower served as a belfry for cathedrals that did not have their own. When the Soviets took power, the bells stopped ringing and the tower became a carpentry workshop. In 1992, the bells were returned to service and, in 2007, the tower complex opened to the public.
The Church of the Twelve Apostles (Церковь Двенадцати Апостолов) was built in 1655 in the far north of Cathedral Square. Originally the private church of Patriarch Nikon, it is connected to the Patriarch’s Palace, where Nikon lived. Originally called the Church of Philip the Apostle, in 1681, Patriarch Joachim rebuilt the church and reconsecrated it for all twelve Apostles. During the rebuild, the Crucifixion was placed above the upper tier of the iconostasis, which had never been done before within Russian Orthodoxy. Today, the church holds several 17th century icons made by famous Russian painters of the time.
The Church of the Deposition of the Virgin’s Robe (Церковь Ризоположения) is named for a famed robe of the Virgin Mary which is said to have miracle-granting powers, especially in times of war. The Church was founded in 1484 by Metropolitan Gerontius. Today, it houses a permanent exhibition of wooden sculptures and carvings from the 15th-19th centuries.
The Terem Palace Churches (Теремные Церкви) is a group of private churches consisting of the Church of St. Catherine, the Church of the Resurrection, the Church of the Crucifixion, and the Verkhospasskii Cathedral (also called the Upper Cathedral of Christ the Savior). “Terem” is an old Russian word for residence. These were built as part of the royal residence.
The oldest church within this complex, the Church of St. Catherine, was built in 1627. The last to be added was the Church of the Crucifixion, completed in 1680. The cluster of churches features eleven golden domes, each of which is on a small, round pedestal on the roof. The cathedral has carved, gilded iconostases with icons dating from the 17th century. Currently, the palace churches are part of the Grand Kremlin Palace, part of one of the official residences of the President of the Russian Federation. They can be accessed by private tour only.
The Church of the Nativity of the Theotokos (Церковь Рождества Богородицы на Сенях) is another private church and is technically the oldest within the Kremlin. It was originally built in 1393 in memory of the Battle of Kulikovo by Princess Evdokia. However, it was badly damaged by a fire and rebuilt in 1479 and again in 1684. It has various architectural elements such as round pillars, apses, and a scapula. It is currently also a part of the Grand Kremlin Palace and accessible by private tour only.
The Kremlin churches provide a beautiful and fascinating glimpse into Russia’s long history, helping to shine light on the deep cultural foundation of the country. They deserve to be a part of anyone’s trip to Moscow.
Above: Arial views of the Moscow Kremlin and other central Moscow locations with a very good view of Cathedral Square.
Grand Kremlin Palace Tour
By Jack Fisher
Formerly the Moscow residence of the Russian tsars, the Grand Kremlin Palace (not to be confused with the State Kremlin Palace) is a complex inside the Kremlin. It now hosts diplomatic meetings and official state ceremonies including presidential inaugurations. It is also designated as a residence of the President of the Russian Federation, but is rarely used for that purpose.
When SRAS gave me the opportunity to take an exclusive tour of this complex, which is an exclusive tour that is normally off-limits to the general public, I had to take it.
This particular tour is different from those that cover the more public areas inside the Kremlin and requires signing up early and submitting your documents for a security check.
I met the tour group on a Friday afternoon in Aleksandrovski Sad, which borders the Kremlin walls. From there, we made our way towards the Kremlin grounds entrance. There was a huge line to get into the grounds through a first security checkpoint, but we were able to skip straight to the front of it since we had registered for our tour ahead of time. Once we were through the gate, the crowd thinned out significantly.
As we walked through the Kremlin grounds, we saw other tour groups taking photos of the landscaping, palace, and other historical buildings. Unlike us, they didn’t have the permission of the Russian government to enter the actual palace. When we got to the palace, we walked through the front doors, crossed a second security checkpoint, met our guide, and started the tour.
Our tour guide inside the building was a woman that worked in preservation. She only spoke Russian, so everything was translated for us by an SRAS-hired guide to English. We began on the first floor of the newer section of the palace and saw several ornate living rooms and guest rooms, followed by the empress’s and emperor’s chambers. Unfortunately, we weren’t allowed to see the emperor’s office and bathroom as President Putin had decided to use them as his personal study for the remainder of his time in office.
After the first floor, we headed upstairs to the second. From the outside the palace appeared to have three floors, but in reality the second floor just had massive, vaulted ceilings and two levels of windows. From what I saw, the second floor seemed to be where the fun happened. The first major room we walked into was the Hall of the Order of St. George, built to house major military meetings and balls and today used as a large conference room. There were names of famous military officers and soldiers inscribed on the walls, and the hall looked like it could hold hundreds of guests. Then it was on to the Hall of the Order of St. Vladimir, which was way less cool. It did, however, have the largest chandelier in the palace, for what that’s worth.
Next, we moved into the oldest section of the palace. It was built in the late 1400s and the newer sections of the palace were built out to connect with it. Our guide told us that by the time of the last czars, the older section was used strictly for ceremonial purposes. The walls were covered with paintings of historical rulers and religious figures. It was definitely my favorite room as there seemed to be an aura of timelessness hanging about the place.
Then we went back through the Hall of the Order of St. Vladimir and through another hall to the older bedchamber of the czar and an older, smaller meeting room for the czar and his nobles. This section was markedly different as there was none of the opulence of the newer palace. It had a utilitarian feel due to its practical layout with comfortable but plain looking chairs, reasonably sized paintings, low ceilings and large traditional Russian stoves.
Finally, we visited the throne room. It was massive, just like the Hall of the Order of St. George, and had polished stone and gilding everywhere. Unfortunately, it was a reconstruction. Our guide let us know that the soviets had torn it apart when they came to power, creating what looked like a massive classroom to house the first meetings of the Soviet Congress. The Russian government had restored it completely within the past decade. She also let us know that the current heir to the Russian throne is Prince Harry of England, which is an interesting fact I’ve been surprising Brits with lately.
On our way out, we exited through a portrait hall. Most of the portraits were typical Enlightenment and Victorian era paintings with stuffy looking people. However, one painting caught my eye: the portrait of Knyaz Sbyatoclav. The man looked absolutely hardcore (and you can see him below in a photo I took).
In my opinion, it was definitely worth $75. While I wouldn’t go twice, the fact of the matter is that you get to see the inside of a beautiful building and stand in rooms that very powerful people meet in and have met in for hundreds of years – which is an opportunity that few regular people are given. Don’t think that it’s too expensive, because you’ll have the experience and memory with you for the rest of your life.
The Kremlin Without a Capital (1712-1918)
By Lee Sullivan
The Kremlin has always been a symbol of Russian power and authority. It is often used interchangeably with the Russian state in journalism and academic literature. This is not surprising considering the Kremlin is situated in the heart of Moscow and has typically housed Russian rulers and their offices – and continues to contain an official residence and office for Russian president Vladimir Putin. However, not all of Russia’s leaders have always called the Moscow fortress home. This article covers the nearly 200 years of Kremlin history when Moscow was not the capital.
Peter the Great moved Russia’s capital from Moscow to St. Petersburg in 1712. Despite the continued crowning of tsars in the Annunciation Cathedral and symbols of power in the Kremlin vaults, Moscow’s role in state life was minimal compared to that of the new capital. This changed when a new stage of construction began under Catherine the Great. Even though St. Petersburg was the new capital, she was crowned in Moscow following ancient tradition. A commission to replace the code of laws from Tsar Alexey Mikhailovich’s time was called in Moscow and its session was held in the Kremlin’s Faceted Palace. This was a sign that under Catherine the Great the state would be ruled from both St. Petersburg and Moscow. Additionally, the Senate was divided into departments under Catherine. Four were in St. Petersburg and two were in the newly commissioned Senate Building, which still stands in the Moscow Kremlin.
Catherine additionally planned a grand reconstruction of the Kremlin interior, one that would have seen most of its buildings demolished, save for the historic cluster of churches, and replaced with modern imperial architecture built with long, straight roads, much like St. Petersburg itself. Demolition was started, including to parts of the original Kremlin walls, when cracks began to appear in one of the cathedral walls due to the resulting disruption of the soil. Because of this, and because of the project’s already enormous cost, it was cancelled, and the original walls re-built.
In September of 1812, French troops occupied Moscow. Napoleon, who led them, planned to occupy the Kremlin as his residence. It is widely thought that in defense against the French, the Moscow mayor ordered fires be set across the city. They raged for days so and were so intense that Napoleon was forced to leave the Kremlin due to the smoke. Upon returning he declared an intention to remain in the Kremlin for winter and ordered additional fortification of the Kremlin walls. However, the French army was weakening due to battle loss and poor supply.
Napoleon ordered his troops to retreat and blow up the Kremlin in the process. Mines were laid but their effectiveness was reduced by rain and prompt Muscovite response. Still, considerable damage was done, including to the Vodozvodnaya Tower, which was completely destroyed.
The Kremlin quickly underwent restoration under Tsar Alexander I and Nicolas I. Despite the war’s considerable drain on state funding, Tsar Alexander I prioritized restoring many parts of the Kremlin including towers, walls, palaces, and cathedrals. He often traveled to Moscow to observe the restoration progress. Many of Russia’s best architects were included in the restoration efforts. Order was progressively restored to the Kremlin and new gardens, now called the Alexander Gardens, were laid out along its exterior. Buildings like the Senate were brought back to their original appearance.
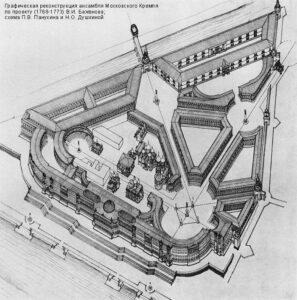
Restoration was completed under Nicholas I, who gave special attention to the restoration of ancient Kremlin churches and other old buildings. He also commissioned the construction of new buildings like the Great Kremlin Palace, after having the old one demolished. The entire imperial family attended the palace blessing during an official ceremony in April 1849. It was constructed and designed with techniques that were ahead of their time – vaulted construction for walls and ceilings, inlaid stone floors, and iron rafters.
Shortly after the revolution, the Communists restored Moscow as the official capital in 1918 when Moscow was reinstated as Russia’s capital. Construction and restoration were completed by the mid-19th century. During the Soviet years, the Kremlin housed Soviet leaders and saw the development and then dissolution of the Soviet state. Today the Kremlin stands in Russia’s capital as a unique architectural ensemble.
The Kremlin Under the Soviets
By Serena Keenan
The new Bolshevik government made sweeping changes to the historic Kremlin complex to, as they saw it, better represent the character of the new socialist state.
During the revolution of November 1917, the Kremlin was ransacked, leaving it with broken glass, destroyed icons, and parts of the complex in disrepair. Restoration of the walls and towers began in 1918, but further restoration stalled for lack of funding and because the communists had not yet decided on a plan for their changes to their seat of government.
The first targets were churches and royal symbols. Nuns and monks who had long lived in the Kremlin were removed. Churches had valuables removed and transferred to the new Commissariat of Finances to fund state projects. Many royal treasures and even crown jewels were similarly transferred. The double-headed eagles on the top of the buildings were promptly removed.
Many buildings were repurposed. Initially, many were converted to housing for Communist functionaries as the revolution and war had depleted Moscow’s housing stock while driving immigration from the countryside to the city. At one point, over two thousand people lived inside the Kremlin. By 1939, however, Kremlin residents consisted of only about three dozen high ranking officials.
Other notable repurposings included turning the Palace of Facets into a canteen with its kitchen inside the Tsarina’s Golden Chamber. The Ivan the Great Bell Tower was turned into a workshop, the Small Nicholas Palace became a worker’s club, and a gym was placed in the Church of St. Catherine. In 1932, the Andrew and Alexander Halls within the palace were gutted to make room for a party congress.
Many of the buildings and statues within the complex were destroyed, often to make way for new construction; only 26 of the original 54 buildings survived the Soviet period. The Chudov Monastery and Ascension Convent were both destroyed to make way for a military academy and eventually the Kremlin Presidium was built on the ground to house the Supreme Soviet, the supreme legislative body of the USSR.
In 1929, the Maly Nikolaevsky Palace, a former royal residence, was replaced by a new administrative building.
In the 1920s, the Russian royals buried in the Archangel Cathedral on the Kremlin’s Cathedral Square were exhumed and autopsied. They and the items in their sarcophagi were turned over to the Kremlin museum. Some valuable artifacts were requisitioned to the state treasury.
In 1935, five stars of rubied glass replaced the double-headed eagles that once topped the Kremlin gate towers.
Throughout WWII, the Kremlin was disguised under mock construction and painted roofs. Despite this, several bombs still fell on the Kremlin grounds, but did not cause major damage.
In 1947, Stalin painted the Kremlin walls red in an unmistakable ode to socialism, a drastic change from the traditional white that the walls had carried for centuries.
In 1955, the Kremlin opened to the public as an open air museum. In that same year, a ban on living in the Kremlin was introduced, lessening any security risk opening it to the public might create.
The last wave of demolitions came in 1958-1961, when the Palace of Congresses, built to house the congresses of Communist Party and cultural events, replaced the Old Amoury and part of the Patriarch’s Palace.
In part due to the outcry from this massive renovation, greater care of the Kremlin grounds began. The official Kremlin museum system was established in 1966, and Elena Gagarin, daughter of Yuri Gagarin, was hired as museum director. Today, that system includes the large armoury, several churches, and items outside of the Kremlin, such as St. Basil’s Cathedral.
The changes made during the Soviet period have left the Kremlin with a striking architectural contrast between traditional, tsarist-era architecture with Soviet-style buildings and the iconic, ancient red walls and remaining cathedrals. Despite the destruction and changes that were carried out, the compound still offers an unforgettable look into Russian and Soviet history that is impossible to get from anywhere else.
The Kremlin Stars
Translated by Caroline Barrow
The following was originally posted to the the Russian 7 website. It has been translated here by SRAS Home and Abroad Translation Scholar Caroline Barrow. Additional edits and updates were applied in 2021.
On October 24, 1935, two long-standing symbols of the Russian monarchy—the two-headed eagles which stood on top of the Kremlin towers, were ordered to be brought down and replaced with five-pointed stars.
Why a five-pointed star became the symbol of the Soviet regime is unknown, but what is known is that Lev Trotsky supported this symbol. Greatly fascinated by the esoteric, he knew that stars and pentagrams have a strong energetic potential and are one of the strongest symbols. The swastika could have easily become the symbol of the new government, since it had a strong following in Russia at the beginning of the twentieth century. Swastikas were displayed on the currency of the temporary government led by Alexander Kerensky, and swastikas were painted on the walls of Empress Alexandra Fedrovna’s Ipatiev House before the royal family was executed there. This swastika trend was stopped almost solely by Trotsky and the Bolsheviks, who opted for the five-pointed star. The history of the twentieth century even showed that stars are stronger than swastikas… Stars shone over the Kremlin, in the place of two-headed eagle.
Erecting the thousand-kilogram stars on the Kremlin towers was not a simple thing to do. The problem was that the needed technology did not exist in 1935. The smallest of the Kremlin Towers, Borovitskaya, rose to 52 meters, and the tallest tower, Troitskaya, reached a height of 72 meters. Throughout the country, there were no tower cranes capable of reaching these heights. However, for Russian engineers, the word “no” did not exist, only the phrase “we must.” Engineers designed and built special cranes that could be installed on the upper deck for each tower. A metal base, called the console, was mounted at the base of each turret window, and on each console the engineers mounted a lifting crane. Thus, the process occurred in several stages: first the two-headed eagles were dismantled, and second, the stars erected.
Each star weighs about one ton. Given the height at which the stars would be placed and the fact that each star has a surface area of 6.3 square meters (potentially excellent for catching the wind), there was a danger that the stars might be blown away along with the top of the towers. So, it was decided to stress test the towers and, it turns out, with good reason: the upper part of each tower and its console was completely destroyed in the process. So, builders reinforced the masonry at the upper levels of the towers, and for the Spasskaya, Troitskaya, and Borovitskaya Tower, metal bracing was added to the base of the tower. The console on Nikolskaya Tower was so damaged that it had to be completely rebuilt.
All the stars were not made identical; four stars differ from one another in their artistic forms. On the Spasskaya Tower star, rays go out from the center. However, on Troitskaya Tower’s star, the rays look like spikes. The star on Borovitskaya Tower is made up of two contours, one inscribed in the other, and, finally, the rays on Nikolskaya Tower’s star have no pattern. In terms of length, the Spasskaya and Nikolskaya Towers were similar, with the distance between the ends of the rays being about 4.5 meters. On Troitskaya and Borovitskaya Towers, the star rays were shorter, and the distance between the ends of the rays was less, measuring 4 and 3.4 meters, respectively.
A star is good, but a spinning star is twice as nice. Moscow is large, its people many, and all must see the Kremlin stars. For the base of each star, special bearings were produced by the First Bearing Plant. These special bearings allow the stars to rotate with the wind even despite their significant weight. Consequently, it is possible to know the direction of the wind given the position of the stars.
Installation of the Kremlin Stars was a true celebration for Muscovites. The stars were not carried under the cover of night to Red Square. The day before the stars were placed on the towers they were put on display in Gorky Park. District and City Secretaries of the Communist Party came together with the ordinary mortals below to see the stars. The stars were lit from the outside to make the Ural stones shine and the rays sparkle. The eagles, taken off the towers, were also displayed to visually demonstrate the dilapidation of the “old” world and the beauty of the “new” world.
The Kremlin stars were not always ruby glass. The first stars, installed in October, 1935, were made from high-alloy stainless steel and red copper. In the center of each star, on both sides, the stars were embedded with precious stones outlining the hammer and sickle emblem. Over the course of a year, the glitter of the gems dimmed. The stars were also found to be too big, not fitting well with the architectural ensemble. In May, 1937, it was decided to install new, illuminated glass ruby stars. Also, they added a star to a fifth tower, the Vodovzvodnaya Tower. The ruby glass was produced at a factory in the city of Konstantinov, according to the method of the Moscovite glassmaker, N. I. Kurochkina. It was necessary to prepare 500 square meters of ruby glass, and for that, a new type was invented—selenium ruby glass. Before that, gold was used to color the glass; selenium was cheaper and produced a deeper color.
The Kremlin stars don’t only rotate, they also light up. In order not to overheat and cause damage, about 600 cubic meters of air is blown through the stars per hour. The stars are not affected by power outages, because they have their own, independent generators.
For the original lighting, the Moscow Electrical Lamp Plant produced the lights for the stars. The stars on Spasskaya, Troitskaya, and Nikolskaya Towers all had 5000-watt bulbs, and the other two operated at 3700 watts. In each star, two parallel filaments were installed. That way, if one burned out, the other filament still shone and a control panel is was notified of the burnout.
To change a bulb, one need not need to climb up to the star. Rather, the bulb comes down on a special rod that runs straight through the bearing. The whole process takes 30-35 minutes. In the stars’ history, the stars stopped shining only twice—once during the war, and another time for the filming of the now-classic movie The Barber of Siberia.
Editorial Note: Update 2021. Starting in 2015, the lighting of the Kremlin stars was updated with one star’s lighting system replaced each year. The old incandescent lamps were replaced with modern metal halide lamps. These lamps are approximately four times more energy efficient than the old bulbs and provide a more intense, higher-quality light. Metal halide lamps are often used for sports stadiums and other places where strong, high-quality light is needed.
In preparation for this switch, Employees of the Central Scientific and Restoration Design Workshops (TsNRPM) measured the illumination of each arm of each star separately to make sure that each would still be lit evenly and brightly. They also created models of the stars lit with various methods including LED matrices and optical fiber. In the end, metal halide was determined to be the closest in historical appearance to the existing incandescent lamps.
Within this update, each star was also given its first compressive maintenance since 1946. Damaged panes were replaced, the stars were cleaned inside and out, and the lubricants within the rotation system were replaced with modern fluids.
The Kremlin Bells in Spasskaya Tower
By Julia Brock
Built in 1491, the Spasskaya Tower is uniquely Russian in its character and historical context, but with other, eclectic features. Designed with the participation of engineers from Milan, Italy, its architectural style borrows from the Italian Renaissance. Its inscriptions documenting its construction are bilingual: in Latin facing toward the outside of the Kremlin, and in the Russian language facing inward.
The tower is arguably one of the Kremlin’s most important sections. Its name in Russian seems to indicate this: Спасская башня, which translates as “Savior’s Tower.” Other towers are named for historical figures, saints, or nearby objects. Savior’s Tower, however, is named for Christ, the central figure for the Orthodox Christian faith that has long played a central role in Russian culture. Further, long used as the main entrance to the Kremlin, it has been associated with Russia’s rulers from the time it was built to Communist times (modern leaders now use the entrance at Borovitskaya, which has more direct road access).
The bells of the iconic Spasskaya Tower peal at regular intervals. The Russian national anthem plays four times a day, and the chimes are broadcast daily at midnight on radio stations to serve as a calibration for Russian time, thus making the Spasskaya Tower Russia’s official timekeeper.
The bells also play for special occasions. They herald the New Year, the most significant secular holiday of the Russian calendar. This receives coverage on television and radio, similar to the media coverage of the countdown ball-drop on New York’s Times Square. The tower clock’s chime at midnight also kicks off church bells ringing in Moscow to recognize the arrival of Easter, which is the Russian Orthodox Church’s main holiday. This official and public event is particularly meaningful to older churchgoers, as the practice of religion came with the risk of punishment during Soviet times.
The gate at Spasskaya Tower is generally perceived as a holy setting. It is topped with an icon of Christ, likely originally added in the 1500’s just over the tower’s main gate. This was later plastered over by the Communists, probably sometime between 1934 and 1939. Some histories indicate that the icon had been ordered to be destroyed and that the workman hired to do it, at great personal risk, instead carefully plastered over it and, in doing so, preserved it for posterity. It was found to be some 80% intact when it was discovered and restored in 2010.
The tower’s clock is currently in its fifth design. The four-sided tower has a clock on each side, with black clock faces and gold hands. The clock sustained damage during the Revolution of 1917 and was restored. The tower does not hold any real flooring, and is instead a hollow structure, although it does have a platform at top for servicing the clock mechanism and bells.
The number of bells has varied over time. Under Catherine the Great, 35 new bells were coordinated with the clock, giving it its greatest historical number. Of these originals, only one is still in service today. The most dramatic change to the bells came when the star was hung on the tower roof in the 1930s. Additional buttressing was needed to support it and all but 17 bells were removed to make way for new structural elements. However, when Spasskaya Tower was renovated from 2017-2020, the structural support was optimized and room made for six more bells, bringing the total to 23. Another six were repaired. This has greatly improved the sound, allowing for a full octave to be played. The new bells were launched for the first time on National Unity Day in 2020.
The State Kremlin Palace
By Benjamin Bradley Mulick
Finished in 1961 after three years of work, the Palace of Congresses, later renamed as the State Kremlin Palace (not to be confused with the Grand Kremlin Palace), opened its doors for the first time for the 22nd Congress of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, welcoming thousands of party delegates as well as communist leaders from around the world. Today, it is still the Kremlin’s newest building and a multipurpose facility, housing large conventions, cultural displays from around the world and even its own ballet troupe. With these functions giving it continued purpose, the Kremlin’s most modern and out of place building is also one of its most significant.
The Kremlin State Palace stands out from the gilded, pastel buildings around it with its hulking angular lines, and large windows divided by tall marble columns. It’s crowned by a glass banquet hall, which was the brainchild of Khrushchev himself.
It features three main halls: The Great Hall, the Small Hall, and the Diplomatic Hall. The Great Hall is the largest, featuring the palace’s main stage and hosting its most important events. With a seating capacity of six thousand, it is where party congresses were held, and where some of Russia’s most prominent cultural programs take place today. The Small Hall hosts smaller musical performances, and by virtue of having removable seating, also hosts dance events, such as the World Cup of Latin American Dance, as held in June of 2021. The Diplomatic Hall provides a smaller and more intimate setting in which to enjoy performances. Last but not least, the Diplomatic Hall often hosts lesser-known artists, often performing genres that do best in closer settings, such as jazz and folk.
The facility also holds many smaller meeting rooms, intended as breakout rooms for conventions, but also used for various purposes today.
The construction of the State Kremlin Palace came with considerable controversy. Not only is it stylistically wildly inconsistent with the rest of the Kremlin’s buildings, one of Russia’s most oldest and most important historical ensembles, but it also resulted in the destruction of several older buildings to make ways for the Palace’s massive presence.
The demolished buildings included the Old Kremlin Armory Building, originally built in 1851 to house the Kremlin’s ceremonial guard and a collection of state documents and treasure. The northern wing of the Patriarchal Chambers was torn down, formerly part of the private quarters of the head of the Russian Orthodox Church.
Because these were officially designated historic buildings, the legality of razing them was questionable and likely would not have taken place had not the decision been made from the office of Khrushchev himself.
Perhaps the real loss, however, came from underground. The original plans for the palace, before the Second World War, envisioned it as truly massive facility built where Christ the Savior Cathedral now stands. In the Khrushchev era, it was planned to build a smaller but still very large building near MGU, along the river, in what were then the still-developing outskirts of the city. When Khrushchev decided to place it inside the Kremlin, its footprint was again shrunk and it faced restrictions on its height so that the view of the Dormition Cathedral would not be entirely lost.
To make up for this, the bottom part of the building was sunk sixteen meters into the valuable archeological depths of the Kremlin’s soil. The buildings torn down to make room for the Palace were themselves built over much older foundations.
Archeologists were given a short window to explore the former Palace of Natalya Narishkina, the mother of Tsar Peter I, as well the former sites of churches, royal kitchens, workshops, and studios in what was once an economic center based within the historic Kremlin.
Teams of archaeologists were assigned to the area, who, in addition to expected finds, also found a number of secret tunnels. Unfortunately, while the archaeologists did their best to learn and preserve what they could, the limited timeframe allowed by the construction of the State Kremlin Palace meant that the archaeological potential of the site was, in large part, wasted. The tunnels were filled in, the old foundations built over, and the ruins lost to history.
Today, the Palace is perhaps best known as the home of The Kremlin Ballet, which was specifically formed in 1990 under esteemed Russian artist and choreographer Andrey Petrov with the purpose of performing there after the Bolshoi Ballet stopped performing at the palace and returned to the Bolshoi, then under renovations.
While the Kremlin Ballet was created with a strong basis in the classics, they have made more recent contributions to the ballet world with a number of their own classically-inspired modern works, including a ballet adaptation of Mark Twain’s The Adventures of Tom Sawyer.
The State Kremlin Palace also hosts the Moscow Classical Ballet, which has been dancing in Moscow since 1966. Demonstrations of this tradition in the upcoming year will include the Moscow Classical Ballet’s dancing reinvention of Romeo and Juliet (which was considered scandalous when it was first performed in 1972), and a performance of Swan Lake, one of Russia’s most important contributions to dance, as performed by the Kremlin Ballet.
Built to hold important political events, the State Kremlin Palace is more a cultural building than a political one. The stage’s relatively short history promises to be subsumed by its promising future. Whatever the next big musical or cultural phenomenon in Russia is, the State Kremlin Palace will be a part of it.
A Tour of the Moscow Kremlin Today
Tour as reviewed by Helen McHenry, 2019
As part of our SRAS cultural program, we were given the opportunity to take a tour of the Kremlin, a historic complex and symbol of the Russian government. We met our guide outside of Red Square before walking along the Kremlin walls to the visitors’ entrance. She pointed out the swallowtail merlons bordering the wall, a design popular in 15th century Italian-style architecture, before we mounted the battlement. To travel behind the Kremlin walls, we crossed a bridge that used to span the Neglinnaya River but today acts as an archway covering part of the footpath.
Inside the Kremlin is an intriguing mix of old and new – from the 15th century walls to the 20th century block of modernism known as the State Kremlin Palace. Our guide informed us of the controversy over the palace’s design, which stands in such contrast to the more traditional styles surrounding it. The building, built under Khrushchev’s leadership primarily as a government meeting hall, has almost as many floors underground as it does above ground. Although many cried out against the building when it was built, it still stands today, where it is now used mainly to host concerts.
A brief walk along a path lined with cannons from the state artillery collection brought us to what appeared to be the mother of all cannons. Indeed, the Tsar Cannon is the largest bombard by caliber ever manufactured and has never been used due to its vast size. Just around the corner lay a similarly large but unused item – the Tsar Bell. Commissioned during the time of Empress Anna, niece of Peter the Great, an almost life-size image of her adorns the bell’s surface.
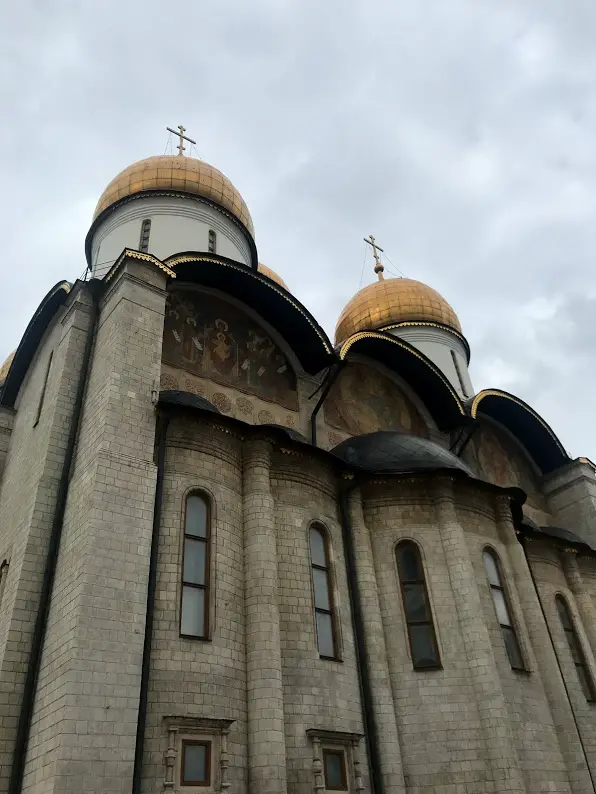

We then traveled to Cathedral Square, which, as its name suggests, features a number of beautiful cathedrals. The overcast day did nothing to accentuate the gold domes that capped their many towers, but no amount of gloom could dim their impressive stature – so immense that photographing them from my vantage point proved a challenge. Each cathedral was adorned with more stunning iconography than the last, overwhelming to the point of monotony as we shuffled through the throngs of tourists.
Our next visit was to the State Armoury, a neoclassical building resplendent with the wealth of the tsars. We traipsed through room after room of riches, from icons, dishware, and diplomatic gifts to clothing, carriages, and thrones. What stood out to me the most was the two distinct – and sometimes warring – natures of Russian identity on display at the Armoury, East and West. The contrast was particularly obvious amongst the collections of clothing, weaponry, and thrones. The older pieces hearkened back to the time before the Western pivot of Peter the Great. While these remained just as ornately decorated as their modern counterparts, they were, on the whole, a lot less outlandish than those done in the styles of the West.
The Armoury marked our last stop within the Kremlin, so we traveled across the city center to the Cathedral of Christ the Savior. Although the cathedral is the world’s largest Orthodox church, the current building is not the original. Christ the Saviour was demolished under the reign of Stalin and was only rebuilt in the late 1990s. Since then, the cathedral has gained fame as the site of Pussy Riot’s 2012 performance, which landed three members in jail for “hooliganism.”
Our guide let us explore the church on our own, as the church requires groups to be led by its own guides. Looking forward to lunch, we opted for a quick pass through the cathedral. Had I not been so hungry, I could have spent hours inside, as every surface held intricately-painted religious imagery intermixed with adornments heavily gilded with gold. Photographs were not allowed within the cathedral, reserving this spectacle to be seen first-hand.
The Kremlin in its entirety is a spot I recommend to all visiting Moscow, as four hours within its walls was not enough for our group to even scratch the surface of the wonders within.
Tour as Reviewed by Joseph Ozment, 2016
As part of SRAS’s Russian as a Second Language (RSL) program at Moscow State University, I had the opportunity to attend a guided walking tour of the Kremlin and its museums. We had a professional tour guide provided by SRAS who was very well informed about all aspects of the Kremlin’s sites and always willing to answer questions.
The tour, as offered by SRAS each session, can differ slightly based on availability and timing. We began our day’s tour not at the Kremlin, but at the nearby Cathedral of Christ the Savior, Russia’s largest Orthodox cathedral and one of the largest Christian structures in the world. Note that there are wardrobe requirements for entering the church (men and women both must have their shoulders covered, while men cannot wear shorts and women must wear skirts at least beneath the knee).
Before going inside, we were taken around the massive structure, and given a brief yet informative overview of its history. We learned that, despite the classical style of the building, it is actually only about 20 years old, having been constructed to resemble the church that once stood on the same ground.
During Communist times, the ground on which the Church now stands was a massive swimming pool, having been filled with water after the original Church was destroyed. The plans that the Communists originally had for the site were to construct the headquarters of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, which would be one of the tallest structures in the world and house the office of the Soviet Union’s premier inside the head of a giant Vladimir Lenin statue adorning the top.
The Cathedral is a truly stunning structure. Comparable only to St. Peter’s Basilica in Rome in my mind, the sheer amount of open air is amazing when one considers how still and tranquil it is on the inside.
We then continued onwards to the Kremlin itself, which was teeming with guided tours from all over the world, just like ours. Seeing other groups from America, but also some from France, Italy, China, and several other European and Asian countries was very interesting, as people tend not to think of Russia as a popular tourist destination. However, tourism here has grown rapidly in recent years, particularly since the ruble lost about half its value on world markets, making Russia a much more affordable location.
Anna informed us of the purposes of all of the first structures we encountered within the Kremlin walls. First of all, though, she made sure that we were aware that the word “Kremlin” does not refer just the center of government in Moscow, but is a general word that means fortress. Most Russian cities and towns of reasonable size and with a medieval history possess a Kremlin.
We saw one of the offices in which President Putin occasionally works, as well as the large, semi-controversial event and concert hall that resides just inside the main entrance to the Kremlin. Despite its modern style that clashes somewhat with the comparatively ancient structures around it, the fact that the building is covered in glass at least ensures that it reflects the beauty and history that abounds within the Kremlin.
After seeing the aptly named Tsar Cannon and Tsar Bell, both of which are two of the largest objects of their kind in the world, and neither of which have been used for their structural purpose in their existence, we moved on to see several of the many churches that stand within the walls of the Kremlin.
Inside the Church of the Annunciation, we were informed of some of the basic components of any Russian Orthodox Church. For starters, every inch of wall is covered in some image or another, from icons of Saints to giant murals that depict judgment day and the people of earth being sent either to heaven or hell. We also learned that the altar in an Orthodox church is given its own room, to which only the priests are allowed entry. The mysticism that is native to Orthodoxy and inherent to its liturgy was embodied in all aspects of these churches.
After our tour of the Kremlin’s outside squares, we were taken on a tour of the Armory Museum, which houses outfits, household items, carriages, armor, weapons, and various sundry items that belonged to the Tsars and Tsarinas of Russia. Anna knowledgeably led us through the various styles worn by different Russian rulers, and explained the significance(s) behind the appearance of what they wore and the carriages in which they rode.
We were in awe of the beautiful jewels that encrusted everything the royals wore and every vessel out of which they drank or off of which they ate, not to mention of the thrones on which they sat. We saw gifts from foreign dignitaries and rulers, and even the museum’s collection of Faberge creations.
All in all, it was a day rich with history and made even more enjoyable by our friendly and incredibly knowledgeable tour guide, Anna. There is hardly a more essential Russian experience to have during your time in Moscow than a guided tour of the Kremlin.
Incidentally, Anna, a guide that SRAS has worked with for years, helps run a guiding collective in Moscow called Bridge to Moscow. They run many private tours and are available for custom tours and travel as well.
Latest Updates
By Josh Wilson
In addition to the changes to how the Kremlin stars are lit and renovations to the Kremlin bells in Spasskaya Tower, for instance, several recent events are of interest.
In the mid-2000s, the Russian Orthodox Church lobbied for the restoration of the Chudov Monetary and the Ascension Convent within the Kremlin walls. The idea was seriously considered and even discussed on television by President Vladimir Putin, although only in the sense of rebuilding them as cultural monuments and part of the museum complex, rather than as working religious institutions. In the end, however, the Kremlin Presidium was simply torn down in 2016 and the area left mostly open with fragments of the old foundations left under glass for viewing. The result is a Kremlin even more dominated by open space and gardens.
Wind has damaged the Kremlin walls on a few occasions. In June 1998, several of the iconic sparrow tail structures on the wall were damaged by strong winds. In April 2018, strong wind damaged the Senate Palace roof. In October 2021, scaffolding being used to restore a section of the inner wall was blown over the top of the wall, also damaging several of the iconic sparrow tail structures. In all cases, the damage was quickly repaired.